News
January 20, 2022
Global Research on Antimicrobial Resistance (GRAM) study
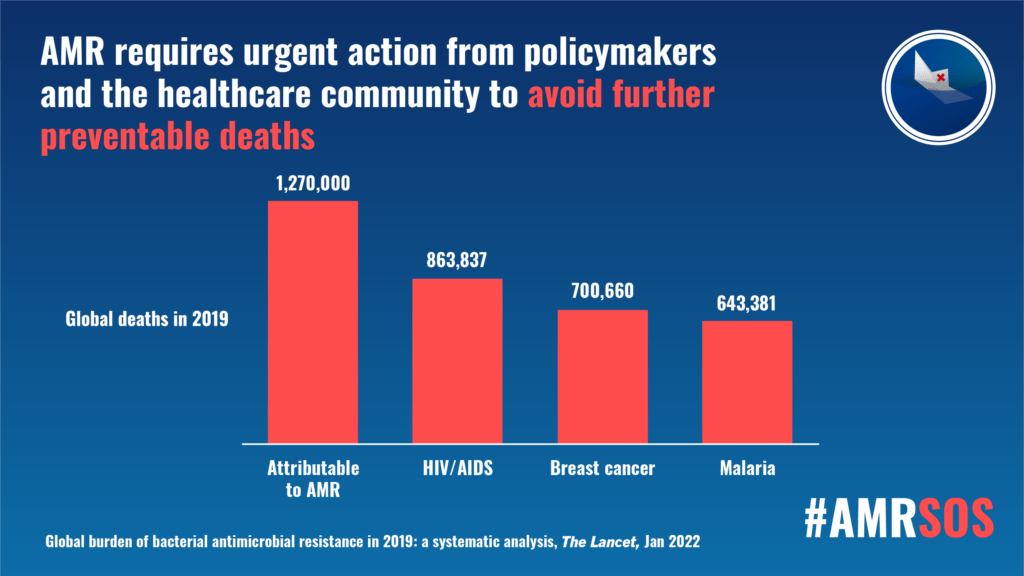
Global Research on Antimicrobial Resistance (GRAM), 4-year study reveals 471 million individual records or isolates and 7585 study-location-years’ worth of data have led to the most comprehensive analysis of the burden of AMR ever undertaken. The study shows that in 2019, 4.95 million people died with drug-resistant bacterial infections. Of these, 1.27 million deaths were directly caused by AMR across the 88 bug–drug combinations evaluated. This makes AMR a leading cause of death globally – higher than HIV/AIDs or malaria – with the highest burdens in low-income settings.
The above article (GRAM) published in Lancet is nicely highlighted in an article by Ramanan Laxminarayan, The overlooked pandemic of antimicrobial resistance